Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsPeacock spider’s radiant rump comes from teeny tiny structures
Male peacock spiders have highly colored hind ends that they shake to attract females. Scientists have now figured out the physics responsible for those hues.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTasmanian devils begin to resist infectious cancer
A deadly contagious cancer is spreading among Tasmanian devils. But the animals are evolving resistance, a new study finds.
-
 Life
LifeScientists watch germs evolve into superbugs
To study how bacteria can evolve resistance to a wide variety of drugs, scientists spread the germs on a food-filled plate the size of a foosball table. Then, they watched resistance rise.
-
 Brain
BrainThese scientists are getting inside your head
You brain might only weigh few pounds, but there’s a whole world in there. Meet the women in science who are digging into the mysteries of the mind.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat is IQ — and how much does it matter?
Studies reveal that intelligence — and success in life — depend on more than what IQ tests measure.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureBananas under attack: Understanding their foes
Fungal blights threaten the world’s most popular fruit. But genetic studies hint at new ways to combat some of these diseases.
-
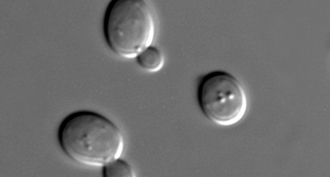 Life
LifeScientists Say: Autophagy
Cells can break down and recycle their parts for later use. This process — called autophagy — won a scientist a Nobel Prize in 2016.
-
 Life
LifeSurprising primate fossils found in an Indian coal mine
Bones of a 54.5-million-year-old primate suggest India might have been a hotbed of early primate evolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsEarthworms: Can these gardeners’ friends actually become foes?
Asian jumping worms can strip leaf litter from floor of U.S. forests, new data show. Many native plants need that leaf litter for their seeds to germinate.
-
 Brain
BrainCool Jobs: Video game creators
Meet an engineer who worked on StarCraft II, an expert building a new kind of reality and a neuroscientist who uses games as brain therapy.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant slugs snack on baby birds
When they accidentally run into bird nests sitting on the ground, some slugs help themselves to a free, easy meal of bird chicks.
-
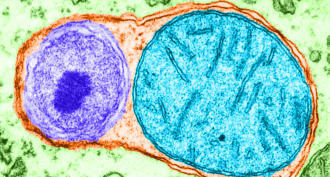 Life
LifeNobel awarded for unveiling how cells recycle their trash
Cell biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi has won the 2016 Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine for discovering how cells take care of housekeeping.
By Meghan Rosen and Laurel Hamers