Life

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Brain
BrainStudy challenges safety for teens of two depression drugs
Scientists reanalyze data on the safety of common drugs to treat depression and find that they don’t seem to help teens. Worse, the drugs may harm them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWolves beat dogs at problem-solving test
When treats are at stake, wolves outperformed dogs at opening a closed container. The dog’s relationship with humans may explain why.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsScientists Say: Xylem
How do trees ferry water from the soil to branches hundreds of feet in the air? This week’s word is the answer.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesNews Brief: People shed clouds of tell-tale germs
Even after someone has left a room, a cloud of his or her germs laces the air, new data show. Watch out: That mix can be very individual — and even ID you!
-
 Animals
AnimalsCool Jobs: Finding new uses for nature’s poisons
Scientists study toxins and other natural compounds in search of alternatives to ineffective antibiotics and dangerous pesticides.
-
 Chemistry
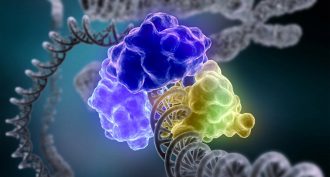
ChemistryTrio gets chemistry Nobel for figuring out DNA repair
Three researchers have won the 2015 Nobel Prize in chemistry for working out how cells fix damaged genetic material.
By Meghan Rosen and Sarah Schwartz -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNobel goes for developing drugs from nature
The 2015 Nobel Prize in medicine went to scientists who used nature as the model for important human drugs to combat malaria and serious infections.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Laura Sanders -
 Animals
AnimalsSperm whales’ clicks suggest the animals have culture
Sperm whales appear to learn the sounds they use to socialize. That suggests they have some form of culture.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentStuffy classrooms may lower test scores
New research links fresh air in classrooms to test scores. Elementary-school students in stuffy classrooms, it found, may perform worse on standardized tests.
-
 Fossils
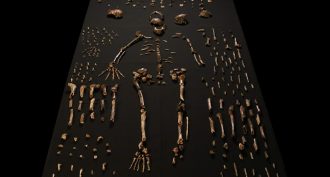
FossilsFossils: Is this new species a human relative?
Fossils found in an underground cave in South Africa may be from a previously unknown species of the human genus, Homo.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsScientists Say: Urushiol
Poison ivy looks harmless, but its oil, urushiol, is not. This is the plant’s oil that leaves an itchy rash or blisters on your skin.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCool Jobs: Finding foods for the future
What's for dinner... tomorrow? Scientists are developing new foods to meet the demands of the growing population in a changing world.