Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: Male-female flexibility in animals
Some animals behave as if they were the opposite sex; others can even change their sex — and still produce offspring.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSugar makes mice sleepy
Sugar may amp up sleep-promoting cells in the brain, a new study in mice finds.
-
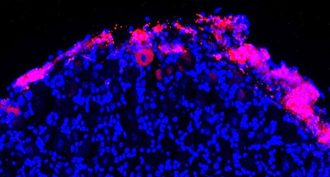 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePain relief could come from a ‘drugstore’ for cells
Mice with nerve damage can be treated for pain with an injection of cells from bone marrow. Scientists have now figured out why this works.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryBacteria become source of ‘greener’ blue jeans
Manufacturing indigo to dye blue jeans now relies on harmful chemicals. But researchers have found a less polluting way to produce the blue tint: bacteria.
-
 Brain
BrainTo protect kids, get the lead out!
Lead poisons hundreds of thousands of children. In Chicago, experts show how the toxic metal hurts test performance in school.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySecret to rose scent surprises scientists
Scientists discovered the molecular tool that roses use to make fragrance. And it wasn’t what they expected.
By Beth Mole -
 Brain
BrainSmell test may detect autism
A new study finds that kids with autism sniff foul scents for as long as pleasing ones. The finding could lead to a test to diagnose the disorder.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy seahorses have square tails
The unique shape of a seahorse tail provides strength, and it may also help the fish to grasp objects.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow this vitamin can foster pimples
Oh no! Vitamin B12 can cause skin bacteria to secrete chemicals that cause zits.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in ivory pinpoints elephant poaching hot spots
Thousands of elephants have been killed for their ivory tusks. A new study used DNA in ivory to trace where most of the killings happen.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew ways to fight the flu
Influenza sickens millions each year. A worldwide epidemic could kill many of them. Fortunately, new ways to fight the flu offer hope — before it’s too late.
-
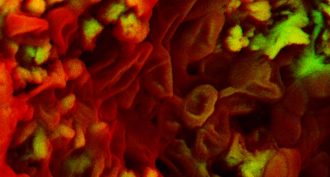 Animals
AnimalsMore dinosaur bones yield traces of blood, soft tissue
More dinosaur bones are found to contain residues of blood and soft tissue. The discovery could help point to when dinosaurs turned into warm-blooded creatures.