Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Autopsy and Necropsy
Sometimes when animals die, they need to be investigated. These examinations have two special names. One is for people, the other for non-human animals.
-
 Plants
PlantsUsing plants to solve environmental problems
Problems in their communities suggested good research projects to three teens. Each wanted to tackle a different issue, from pollution to world hunger. To learn more about these issues, they turned to their local ponds, wetlands and gardens.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists Say: Taphonomy
Studying what happens to plants and animals after they die can teach us about ecosystems and evolution. This study has a special name.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis is no cold fish!
The opah is the fish closest to the whole-body warm-bloodedness typical of mammals and birds. This trait may give the species an edge in the ocean’s cold depths.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesThe bugs within us
Hordes of bacteria live inside people and other animals. This ‘microbiome’ can affect the development of the blood-brain barrier, food choices — even mating.
By Roberta Kwok -
 Brain
BrainStudying? Don’t answer that text!
Homework time? Put away the cell phone. Responding to texts gets in the way of learning and test-taking, teen researchers show.
By Sid Perkins -
 Plants
PlantsPicture This: The world’s biggest seed
This monster seed develops on a super-slow-growing island palm. Key to that palm’s survival are leaves that funnel fertilized water to nutrient-starved roots.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCatching ZZZs may retrieve lost memories
Forgetful? Maybe you’ve forgotten to get enough shuteye. A study in fruit flies suggests that a good sleep can boost their ability to remember things.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPesticides offer bees a risky allure
Honeybees and bumblebees sometimes cannot taste or avoid pesticides called neonicotinoids. And that may expose some of these important pollinators to harm.
By Susan Milius -
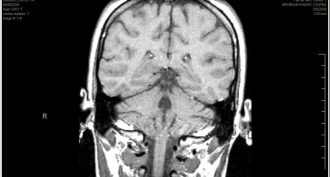 Brain
BrainScientists Say: MRI
MRI is a technique used to diagnose diseases and to study the body. The machine can map internal structures, all the way down to tiny blood vessels.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPicture This: The real ‘early bird’
Long before dinosaurs went extinct, birds were emerging on Earth. These hummingbird-size wading birds are the earliest known ancestors of today’s birds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsReturn of the bed bug
Bed bugs have staged a comeback over the past 15 years. The bloodsucking parasites succeeded through a combination of evolution and luck.
By Brooke Borel