Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: Eek — what if you get bed bugs?
A bed bug infestation requires attention. Some treatments you can undertake yourself, but many are best left to professionals.
By Brooke Borel -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists feed bed bugs (on purpose)
To study bed bugs in the lab, scientists had to first learn how to keep the blood-thirsty critters well fed. And that proved easier said than done.
By Brooke Borel -
 Animals
Animals4 reasons not to ignore signs of bed bugs
Here are important reasons not to ignore signs of bed bugs. Above all, an infestation carries real risks to your health and wellbeing.
By Brooke Borel -
 Brain
BrainHands-free but still distracted
When people aren’t distracted, they can see a traffic light change very quickly. But a teen scientist now shows that texting — even with a hands-free device — gets dangerously slow.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat’s the buzz? A new mosquito lure
Broadcasting a fake buzz can lure male Aedes aegypti mosquitoes away from females. That could reduce populations of these annoying — and disease-causing — insects, reports a teen at the 2015 Intel ISEF competition.
By Sid Perkins -
 Brain
BrainBack off, bullies!
Mental health is another reason to stop bullies. Victims of bullying are more likely to develop anxiety problems than are victims of abuse or neglect, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDo mosquitoes love you? Blame your parents
By studying twins, scientists found that how attractive we are to mosquitoes depends partly on our genes. That could lead to better bug repellents.
-
 Brain
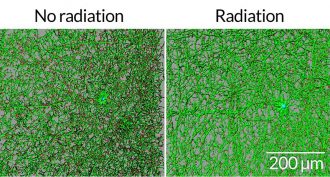
BrainTrip to Mars could damage astronauts’ brains
Experiments in mice suggest the high-energy particles that would zap astronauts on a mission to Mars could leave the explorers with brain damage.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat’s for dinner? Mom.
Female spiders of one species make the ultimate sacrifice when raising their young: The mothers feed themselves to their children.
By Susan Milius -
 Fossils
FossilsRitual cannibalism occurred in Stone Age England
Stone Age human bones from a cave in England show signs of cannibalism. The people had been eaten during burial rituals nearly 15,000 years ago, experts say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Brain
BrainTwisters: Can warning people too early backfire?
If people think they have enough time to flee a tornado, they may try to drive away, information shows. This could leave them stuck in traffic — with no protection — when the storm does show up.
-
 Fossils
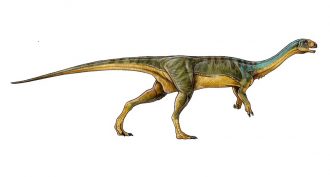
Fossils‘Frankenstein’ dino showed a mashup of traits
New species unearthed in Chile is “an anatomical Frankenstein,” declares one of its discoverers.