Life
-
 Fossils
FossilsDino double whammy
Most scientists think an asteroid helped kill off the dinosaurs. But new calculations suggest that asteroid might have gotten some help from a long series of volcanic eruptions in what is now India.
-
 Animals
AnimalsElectric eels get on their prey’s nerves
Electric eels wield remote control over their prey’s muscle movements. They do this by zapping their nervous system. Experiments suggest the creatures use these paralyzing bursts of energy to hunt, too.
-
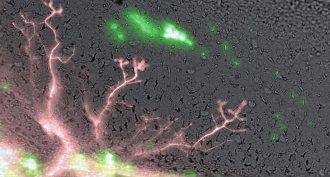 Animals
AnimalsA nervy strategy for transplants
Adjusting the electric charges in cells helped a transplanted eye reach out to its new host. The eye grew cells, which help transmit signals to other cells.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesClouds may be dining cars for some germs
Scientists had known microbes could hitchhike across and between continents on clouds. New research now shows that some germs don’t just treat clouds as a high flying jet, but also as a cafeteria.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentSpidey sense: Eight-legged pollution monitors
Spiders that prey on aquatic insects can serve as sentinels that naturally monitor banned chemicals that still pollute many rivers across the United States.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesVirus blamed in starfish die-off
A virus may explains the deaths of millions of starfish along the Pacific Coast of North America. The deaths affect 20 species. Some of the stricken animals appear to melt into puddles of slime.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentNano air pollutants strike a blow to the brain
Most people think that air pollution poses the biggest risk to our lungs. In fact, pollution hits the brain too, sometimes by traveling a direct route — through our noses. These tiny pollutants can harm IQ and more.
-
 Brain
BrainBanned drug reduces brain communication
Illegal drugs called “bath salts” can reduce communications among different brain regions. New research, done in rats, may explain the violent and unpredictable behavior seen in some people using these drugs.
-
 Brain
BrainScents may affect how appealing tobacco is
Menthol’s effects on the brain may make tobacco more addicting. In contrast, foul odors might help smokers quit. Two new studies show how.
-
 Fossils
FossilsDinos: Some were ‘marathoners’
The arrangement of major muscles in a duck-billed dinosaur’s legs would have helped them outrun predators such as T. rex, a new analysis suggests.
By Sid Perkins -
 Fossils
FossilsTar pit clues provide ice age news
New analyses of insects and mammals trapped in the La Brea Tar Pits point to climate surprises during the last ice age.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsTiny — but mighty — food-cleanup crews
Discarded food wastes can turn city spaces into food courts for disease-carrying rats and pigeons. But a new study shows tiny cleanup crews — especially pavement ants — are doing their best to eliminate such wastes. This, in turn, makes cities less attractive to bigger pests.