Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew frog discovered in New York City
This animal could almost be mistaken for the southern leopard frog — until it opens its mouth. The call the males issue has proven unique.
By Janet Raloff -
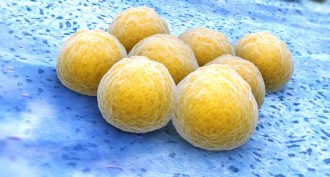 Microbes
MicrobesGerms help each other fend off antibiotics
Drug-resistant bacteria can cause persistent infections. A new study finds these germs fight drugs in different ways. And they can swap various compounds, increasing their neighbors’ chances of overcoming the drugs meant to kill them.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCleaning with greens
Cleaning up toxic waste is a big and expensive problem. Scientists have tinkered with the genes in some plants. Now those greens can take on this dirty work. Still, they're not quite ready for prime time.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFish just wanna have fun
Although biologists have observed fish playing before, scientists have now recorded hours of video showing a new type of antic in fish.
-
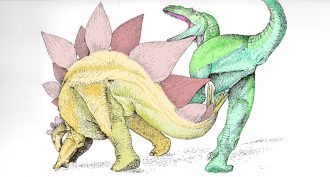 Fossils
FossilsSpiked tail to the rescue!
A stegosaur’s bony ‘armor’ didn’t just fend off a predator’s teeth. The tail spikes could gore attackers, ultimately killing them, fossils now show.
By Sid Perkins -
 Environment
EnvironmentWill water woes leave Americans thirsty?
In the United States, people often assume that clean water will always be available. But factors ranging from global warming to pollution have begun threatening drinking-water supplies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTeen studies living flashlights of the deep
A teen studies a cryptic fish to better understand when and why it flashes its bacterial glow.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePills of frozen poop fight killer disease
Popping poop pills? Of course it sounds yucky. But researchers find it might just be one of the most effective ways to knock out a very serious — and tough-to-kill — intestinal disease.
By Janet Raloff -
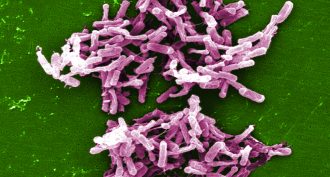 Microbes
MicrobesExplainer: What is C. difficile?
Over the past two decades, these severe bacterial infections have evolved from a no-big-deal occurrence to a common, life-threatening problem.
By Janet Raloff -
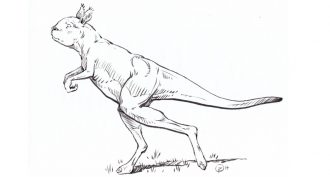 Animals
AnimalsNews Brief: No hopping for these ancient ‘roos
By hopping, today’s kangaroos can scoot swiftly through the countryside. That was not true for some of their ancient cousins. True giants, those now-extinct kangaroos would have walked on two feet — and relied on their tippy-toes.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsComing: The sixth mass extinction?
Species are dying off at such a rapid rate — faster than at any other time in human existence — that many resources on which we depend may disappear.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStrong body helps the mind
Study finds new link between the body and brain in mice and may help explain how exercise heals.