Life
-
 Health & Medicine
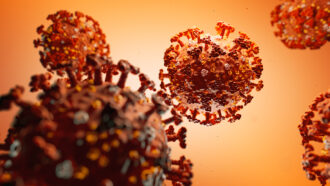
Health & MedicineA Hong Kong man got the new coronavirus twice
His is the first confirmed case of reinfection with this virus. His second bout was detected by accident, because he showed no symptoms.
-
 Fossils
FossilsAmerican crocs seem to descend from kin that crossed the Atlantic
A fossil hints that early crocodiles crossed over from Africa, millions of years ago, to colonize a new land.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureScientists Say: Carbohydrate
Carbohydrates are molecules with carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. Animals break down these chemicals in food to get energy.
-
 Brain
BrainYou don’t see as much color as you think
It might seem like we live in a world full of color. But when scientists flip it into black and white, most people never notice the switch.
-
 Humans
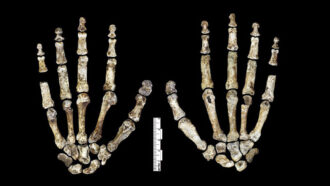
HumansLet’s learn about early humans
Homo sapiens are the last member left of our genus. But many other species of early humans existed before us.
-
 Animals
AnimalsViral scents? Dogs sniff out coronavirus in human sweat
Researchers train dogs to sniff out COVID-19. In the United Arab Emirates, sniffer dogs have already begun identifying infected passengers at airports.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTo figure out your dog’s ‘real’ age, you’ll need a calculator
What’s your dog’s human-equivalent age? Just multiply how old it is times seven, right? Uh, no. And here’s why.
-
 Animals
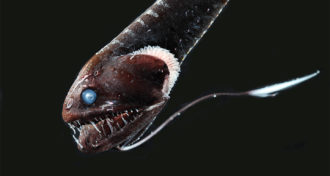
AnimalsSuperblack fish can disappear in the deep sea’s darkness
Some fish that live in the ocean’s depths are superblack due to a special layer of light-absorbing structures in their skin.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins can learn from their peers how to use shells as tools
Some bottlenose dolphins seem to look to their peers, rather than mom, to learn how to trap prey in shells.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Physics
PhysicsFlying snakes wriggle their way through the air
Flying snakes go tens of meters (yards) without wings. They do it by undulating back and forth and up and down, a new study shows.
-
 Fossils
FossilsEarly dinosaurs may have laid soft-shelled eggs
Scientists for the first time have turned up evidence of fossils from soft-shelled dinosaur eggs. This has scientists rethinking how dinosaur eggs evolved.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists Say: Deforestation
Trees slurp up carbon dioxide and help keep our planet cool. But deforestation cuts those trees down in large numbers.