Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy are bird eggs in cold climates darker colored?
A global survey of bird egg color has revealed a simple trend: the colder the climate, the darker the egg.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists look to hack photosynthesis for a ‘greener’ planet
Photosynthesis turns sunlight into energy for plants. Scientists want to know more about it, imitate it — even improve it.
-
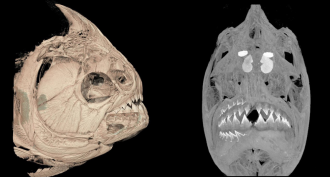 Animals
AnimalsPiranhas and plant-eating kin replace half their teeth at once
Piranhas and pacus shed and replace half of their teeth at a time. New teeth lock together as they push up from the jaw.
-
 Life
LifeA new spin on lab-grown meat
A technique inspired by how cotton candy is spun could help produce lab-grown meat at a lower cost and on a bigger scale.
-
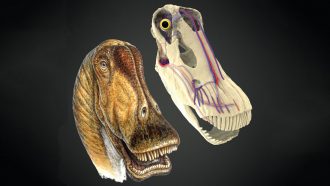 Animals
AnimalsBlood vessels in their heads kept big dinos from overheating
Giant dinosaurs evolved several ways to cool their blood and avoid heatstroke.
-
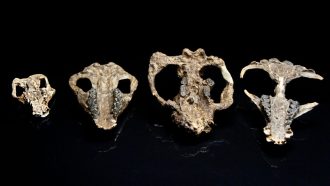 Fossils
FossilsFossils show mammals’ rise to dominance after the dino-killing asteroid
What happened to mammals after an asteroid wiped out the dinosaurs? Newfound fossils show how they grew in size, eventually dominating much of life on Earth.
-
 Tech
TechWeird little fish inspires the development of super-grippers
Suction-cup designers were inspired by the rock-grabbing tricks of the aptly named clingfish.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsHumpback whales catch fish using bubbles and flippers
Scientist for the first time have captured details of humpback whales’ hunting tactics on camera.
By Sofie Bates -
 Animals
AnimalsCongolese toads may avoid predators by copycatting deadly vipers
If Congolese giant toads are mimicking venomous Gaboon vipers, this would be the first reported case of a frog imitating a snake.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Species
This word describes organisms grouped by their similarities in genetics and physical traits. But defining species can be tricky.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNewly discovered eel sets a jolting record for animal voltage
Scientists have found two new electric eel species. One now holds the animal kingdom’s record for highest delivered voltage.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe moon has power over animals
The moon is known for its tidal effects. But its light also can exert a powerful influence on animals large and small.
By Erin Wayman