Materials Science
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Pigment
From fruits to fur to fine art, many materials get their colors from compounds called pigments.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about diamond
Diamond is born under extreme heat and pressure inside Earth and elsewhere in the universe.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceScientists Say: Silicone
Silicone is a generic term for a whole slew of humanmade polymers with many different forms and applications.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryReusable plastic bottles release hundreds of pollutants into water
Data show the plastic ends up tainting drinking water. For now, scientists don’t know what health risks downing these pollutants might pose.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLet’s learn about cellulose
The world’s most abundant natural polymer is finding all kinds of new uses, in everything from ice cream to construction.
-
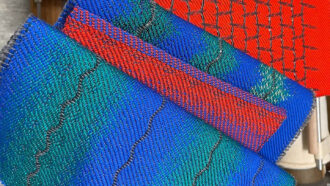 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThis new fabric can ‘hear’ sounds or broadcast them
With special fibers that convert tiny vibrations to voltages, a new fabric senses sound. Someday, such fabrics could monitor the body or aid hearing.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about the future of smart clothing
Researchers are fashioning new materials to make clothes more comfortable and convenient.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceNew cloth cools you when you’re hot, warms you when you’re cold
Scientists 3-D printed the new fabric, which has even more tricks up its sleeve — such as conducting electricity and resisting radio waves.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceEngineers borrow a tree’s cellulose to toughen new materials
Cellulose gives plants their strength. Engineers are turning this renewable, environmentally friendly resource into brand new materials.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA disinfectant made from sawdust knocks out deadly microbes
It’s made by pressure-cooking sawdust and water, is cheap and easy to make — and could lead to greener cleaning products than chemicals used today.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryNew process can transform urban CO2 pollution into a resource
Researchers have developed a liquid metal that breaks down carbon dioxide in the air, converting it from a climate threat into a valuable raw material.
-
 Environment
Environment‘Mining’ cryptocurrencies pollutes the real world
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies exist only online. Yet the environmental impacts of their networks affect the real world.