Physics

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Materials Science
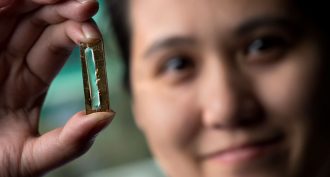
Materials ScienceNanowires could lead to super-long-lived battery
Scientists have long been looking for ways to make rechargeable batteries that last forever. They now may be close. Their solution: gel-dipped nanowires.
By Lela Nargi -
 Earth
EarthCool Jobs: Getting to know volcanoes
It’s too hot to explore the insides of a volcano. These scientists examine their lava, their low-frequency rumblings and their ‘vog’.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Animals
AnimalsInsects can patch their broken ‘bones’
When insects suffer wounds, they can mend their ‘skeleton’ with a patch on the inside. This makes the leg strong again, new data show.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPossibility of strange new particle surprises physicists
Last winter, physicists at the Large Hadron Collider detected hints of a particle beyond their wildest dreams. Soon they may learn if it’s real.
-
 Tech
TechHow to make window ‘glass’ from wood
Scientists have come up with a way to make wood transparent. The new material could be used in everything from windows to packaging.
By Sid Perkins -
 Physics
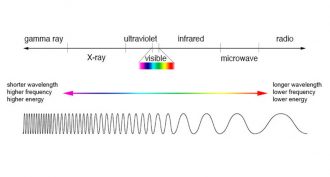
PhysicsScientists Say: Frequency
The distance between one wave peak and another is wavelength. But how fast those peaks are moving along is frequency.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSunlight + gold = steaming water (no boiling needed)
Nano-gold is the new black, at least when it comes to absorbing heat. When tiny gold particles get together, they become energy super-absorbers — turning them black.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Yottawatt
On Earth, scientists measure energy use in watts. When you have lot of those watts — one million billion billion — you have a yottawatt.
-
 Tech
TechFeeling objects that aren’t there
A new technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create virtual objects you can feel. Its uses include better video games and safer driving.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Wavelength
When something travels as a wave — such as light — scientists can measure it by its wavelength, the distances between the peaks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy Paralympic sprinters have trouble with curves
Whether an artificial leg is on the right or left side of the body may affect how fast runners can take a turn.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySmash hit: Making ‘diamond’ that’s harder than diamonds
Scientists had suspected extreme meteorite impacts might turn graphite into an unusual type of diamond. Now they’ve seen it happen — in under a nanosecond.
By Beth Geiger