Physics

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Environment
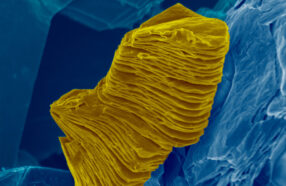
EnvironmentNew ultrathin materials can pull climate-warming CO2 from the air
To slow global warming, we’ll need help from CO2-trapping materials. Enter MXenes. They’re strong and reactive — and they love to eat up CO2.
By Shi En Kim -
 Physics
PhysicsHeat makes water evaporate. Now it appears light can, too
In the lab, shining light on water made it evaporate faster. This never-before-seen effect, if real, might be happening naturally all around us.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA new tool shows tiny changes in the ’24-hour’ length of a day
An underground instrument known as ‘G’ uses laser beams to measure Earth’s rotation — a gauge of day length — with extreme precision.
-
 Tech
TechParticles from tree waste could prevent fogged lenses, windshields
A new coating made from a renewable resource — water-loving nanoparticles made from wood — could keep glass surfaces fog-free.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExperiment: How well do different materials create static electricity?
Why are some materials more susceptible to static cling than others? Investigate by making your own electroscope.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Gamma ray
Lightning bolts, nuclear explosions, colliding stars and black holes all throw off this high-energy type of light.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new hydrogel could help pull drinking water from the air
The salty gel absorbs more water from the air than similar gels, even in desert climates. This could provide clean water for drinking or farming.
By Laura Allen -
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Ultrasonic
This word describes sound waves that have frequencies too high for human ears to hear.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSkipping stone physics could aid net-tangled whales and more
The unexpected movement of buoys and spheres in water could lead to redesigns for fishing nets and ships.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhere does Godzilla get his atomic breath?
Some secrets of the kaiju’s atomic breath can be explained with creative applications of physics and biology.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Supercool
When a liquid is supercooled, it has been chilled below its freezing point without freezing.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCreation of quantum dots wins 2023 chemistry Nobel
The award honors three scientists who discovered and built quantum dots, which are now used in everything from TVs to medical tools.
By Carolyn Gramling and Tina Hesman Saey